We’ve been hearing a lot about carbs lately, how they are good to eat, bad to eat, and everything in between. Carbohydrates are one of three essential nutrients: fat, protein, and carbohydrates. All three are necessary for physical health, but not all three affect all people the same way. For example, those with diabetes need to monitor their carbohydrate intake in order to maintain healthy blood glucose levels. Let’s take a look at carbohydrates and how they can impact glucose levels.
Carbohydrates can besimple or complex.
- Simple carbohydrates are digested easily, which can raise blood sugar quickly. Foods that are primarily simple carbohydrates include sugar, syrups, cookies, white bread, white rice, and regular pasta.
- Complex carbohydrates have more fiber and are digested more slowly, keeping blood sugars from spiking. Most vegetables and whole grains are complex carbohydrates.
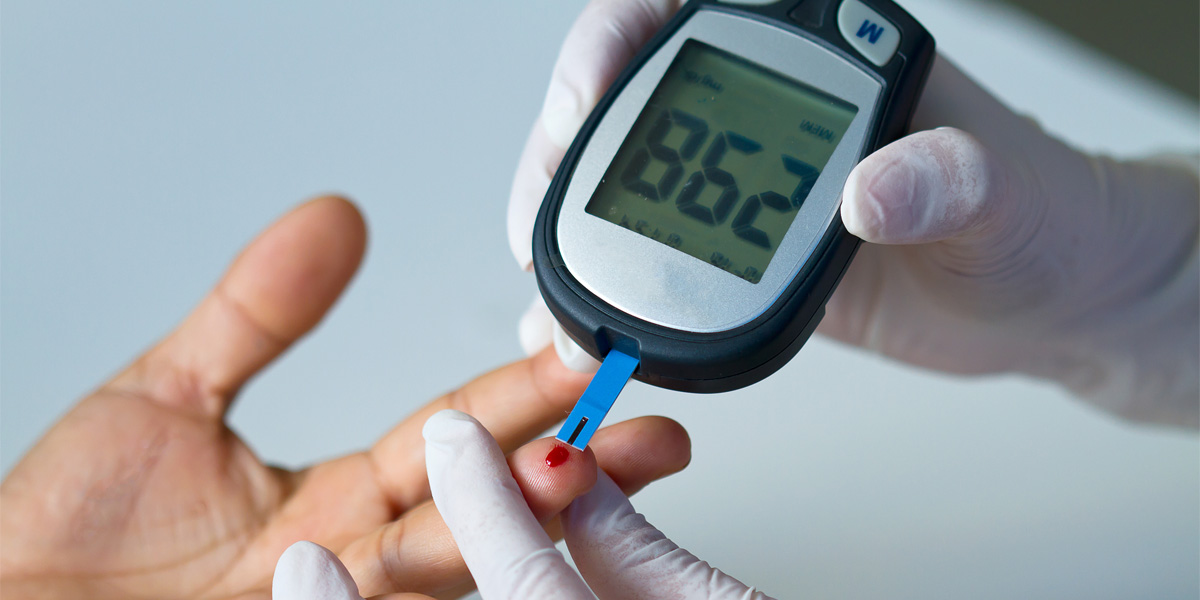
When we eat carbohydrates, our bodies break them down into sugars. When blood sugars (glucose) rise, the pancreas produces insulin, which helps the glucose enter the cells to provide energy. For those with diabetes, insulin is not produced, or not enough insulin is produced, and the glucose in the bloodstream remains high. Elevated blood glucose can do long term damage to the body, and significantly elevated blood glucose can cause a coma or even death.
Diabetics need to manage carbohydrates carefully.
- Those with type 1 diabetes need to balance their carbohydrate intake with their insulin intake.
- Those with type 2 diabetes need to focus on complex carbohydrates and are often advised to limit the amount of carbohydrates at each meal and snack. Carbohydrates are an important form of energy, but it is easy to consume too many of them. Read all labels for added sugars and limit baked goods and treats. Enjoy whole fruits and vegetables, which contain necessary fiber, and try to have some protein with your carbohydrate. If you are diabetic, ask your doctor for the best way to monitor your blood glucose and carbohydrate intake.